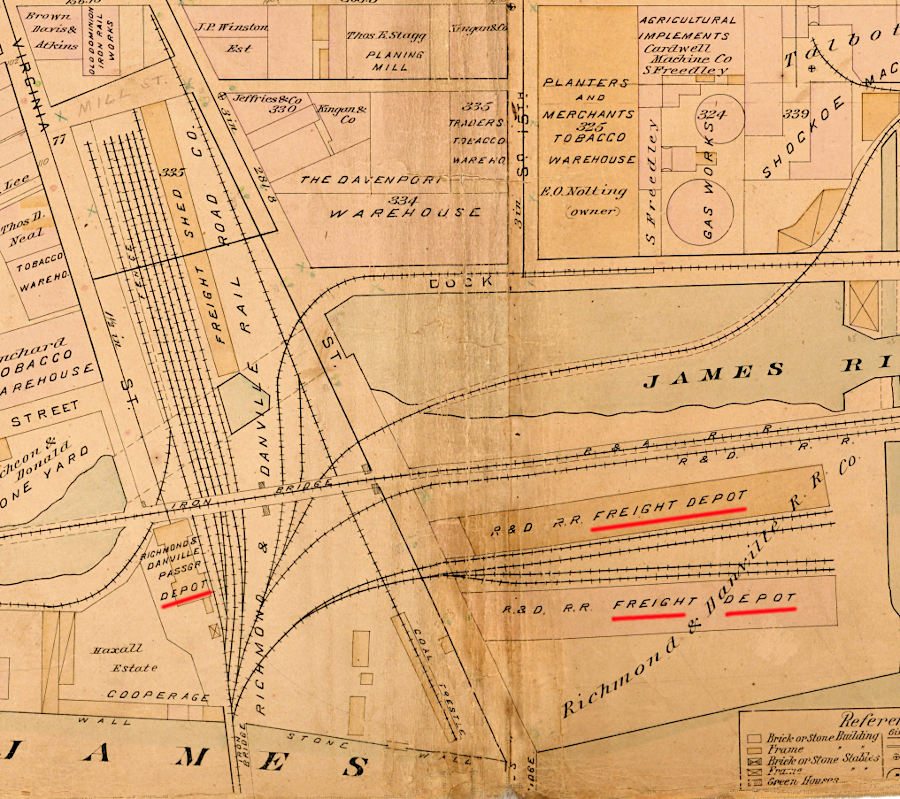
the Richmond and Danville Railroad's passenger and freight depots in 1889, on 14th Street next to the Turning Basin in Richmond
Source: Virginia Comonwealth University, Baist Atlas of Richmond - Outline & index map Richmond and vicinity (1899)

the Richmond and Danville Railroad's passenger and freight depots in 1889, on 14th Street next to the Turning Basin in Richmond
Source: Virginia Comonwealth University, Baist Atlas of Richmond - Outline & index map Richmond and vicinity (1899)
The General Assembly chartered the Richmond and Danville Railroad on March 9, 1847. The bridge across the James River linking Manchester to Richmond was built in 1850.
A short branch along the James River to Belle Isle, with a bridge to the iron works there, was completed in 1851. Slightly upstream, another branch served the Westham granite quarries.
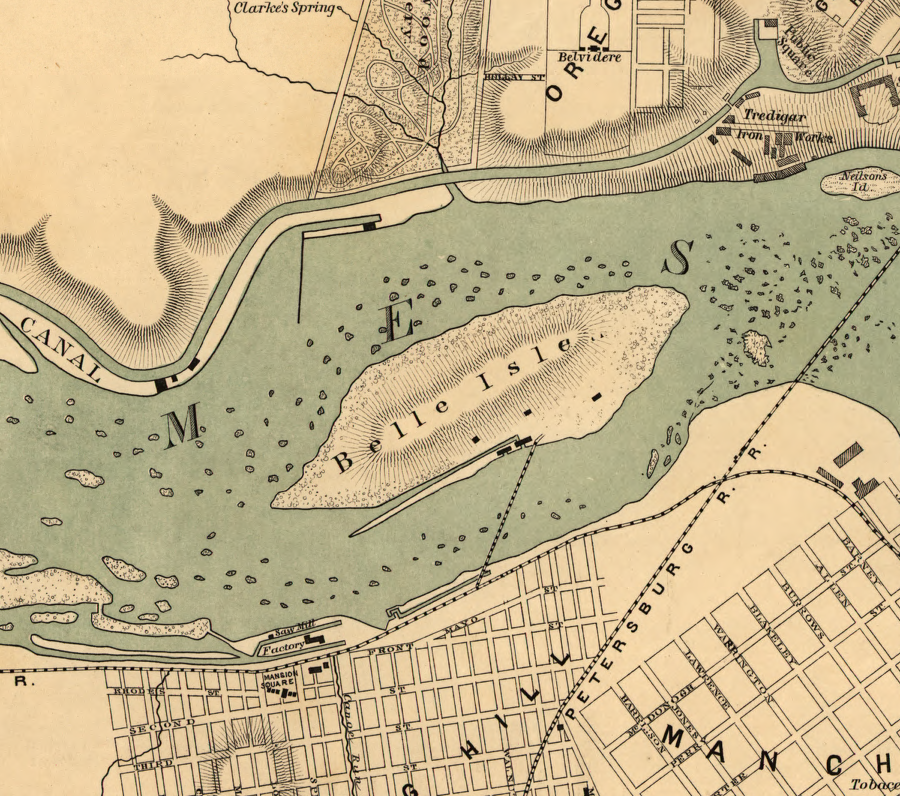
the Richmond and Danville Ralroad built a short branch to Belle Isle in 1851
Source: Library of Congress, Map of the city of Richmond, Virgini (by US Coast Survey, 1864)
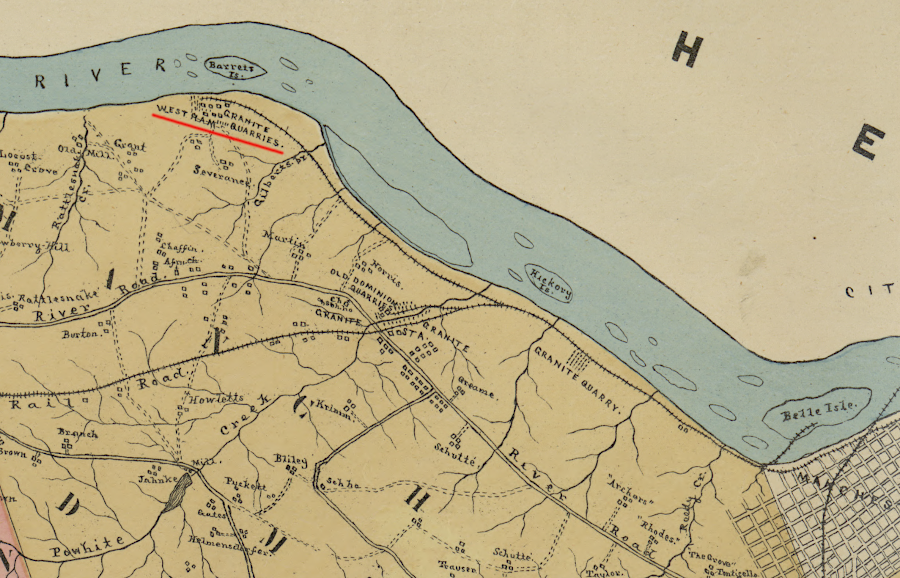
the Richmond and Danville Railroad built a branch line to the Westham granite quarries in Chesterfield County
Source: Library of Congress, Map of Chesterfield County, Va (by Joseph Edgar LaPrade, 1888)
In 1850, track reached Coalfield Station in Chesterfield County. The gravity-powered Chesterfield Railroad ceased operating when the steam-powered Richmond and Danville Railroad reached the mines and captured the coal-hauling business. The owners of the Chesterfield Railroad set a high price on their stock, so the Richmond and Danville Railroad declined to purchase it and built their own spur to the mines in 1854. In 1858, the Richmond and Danville Railroad made its only payment to the Chesterfield Railroad, purchasing its real estate along the James River betwen the coal wharf and Manchester.
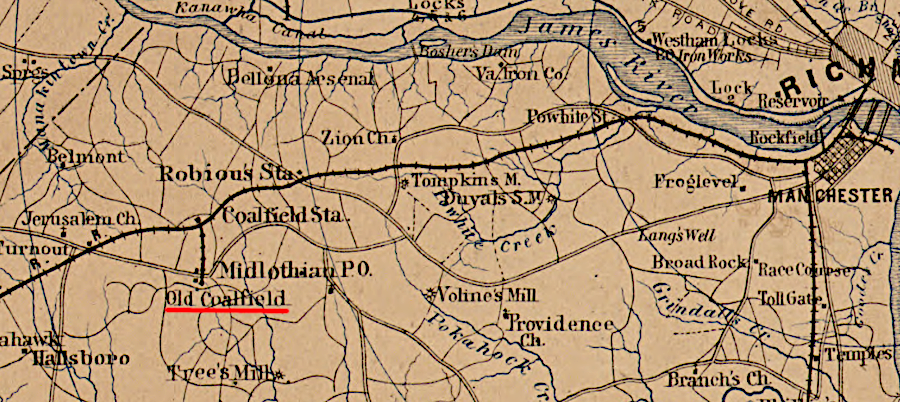
the Richmond and Danville Railroad reached the Chesterfield County coal mines in 1850, and built a spur to the mines in 1854
Source: Library of Congress, Thirty five miles around Richmond, Va (by Jedediah Hotchkiss, 1867)
Four mortgages were required to raise the funds necessary to build the 140 miles of track connecting the two cities, which was completed in 1856. That year the railroad obtained authorization from the legislature to build an extension west from Danville, across the Blue Ridge, to connect with the Virginia and Tennnessee Railroad. The network of rails controlled by the Richmond and Danville Railroad was enlarged later, but the only construction from Danville to the west was accomplished in 1880-82 by the Danville and New River Railroad.1
Barbara Irene Burtchet, "A history of the village of Midlothian, Virginia, emphasizing the period 1835-1935," University of Richmond Masters thesis, May 1983, pp.46-47, https://scholarship.richmond.edu/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=1491&context=masters-theses; Fairfax Harrison, A History of the Legal Development of the Railroad System of Southern Railway Company, 1901, pp.83-87, https://books.google.com/books?id=0IkjAQAAMAAJ (last checked July 3, 2020)
In Richmond, the railroad's James River roundhouse and freight docks were on the south bank. A bridge across the upstream edge of Mayo's Island crossed the James River to a depot along the Tidewater Connection locks of the James River and Kanawha Canal.
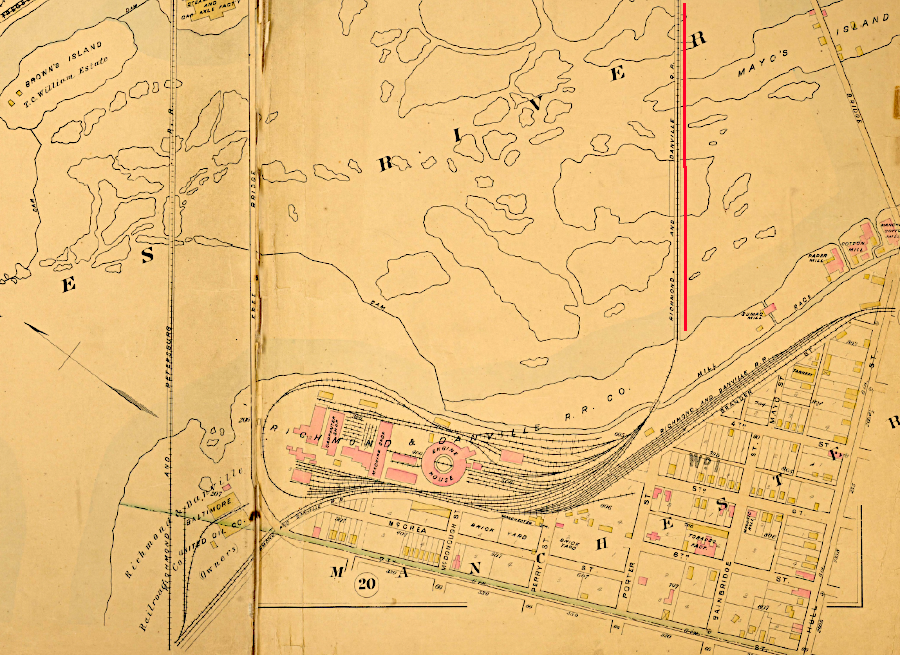
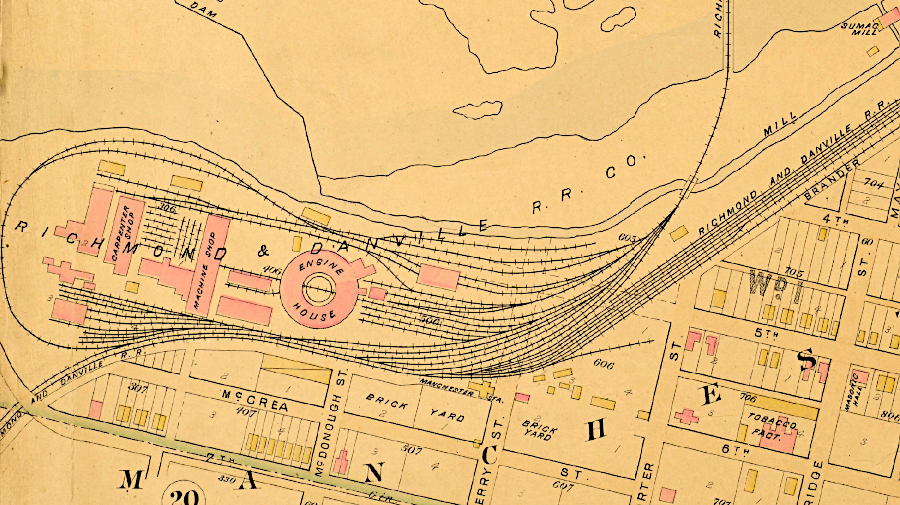
the Richmond and Danville Railroad yard and roundhouse were on the south bank of the James River
Source: Virginia Commonwealth University (VCU), Baist Atlas of Richmond, VA (1889)
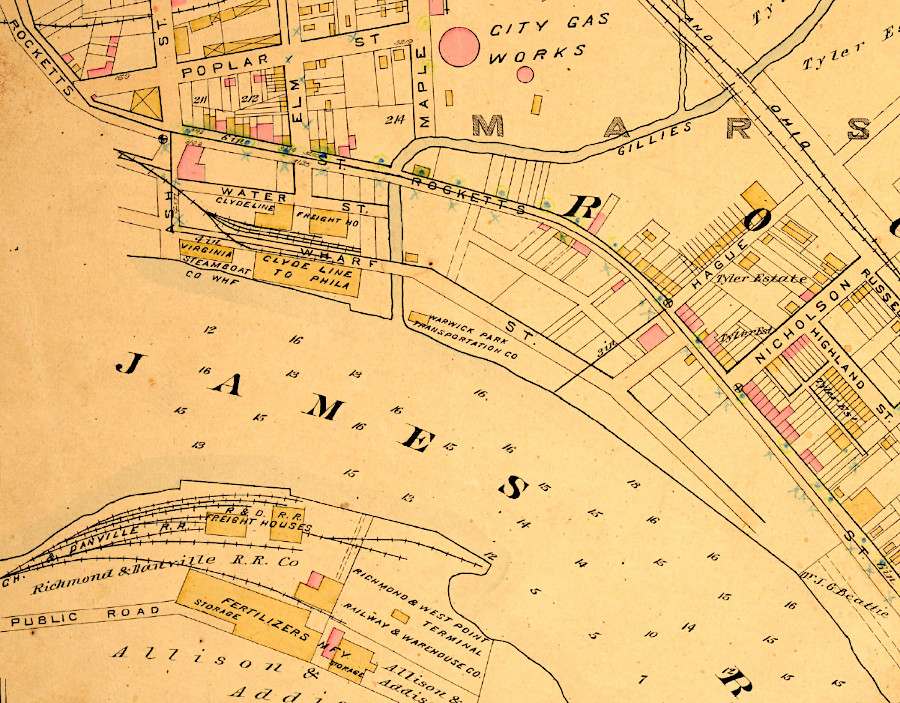
the Richmond and Danville Railroad freight docks were on the south bank of the James River, opposite Gillies Creek
Source: Virginia Commonwealth University (VCU), Baist Atlas of Richmond, VA (1889)
The southern destination of the Richmond and Danville Railroad was on the Dan River, a tributary of the Roanoke River. Farmers in the southern Virginia Piedmont shipped their agricultural products by wagon to Lynchburg or Petersburg, or down the Roanoke River via batteaux to Weldon. At Weldon, rival railroads could send the freight to either Petersburg or Portsmouth.
The Richmond and Danville Railroad made transportation to a new port city feasible, and significantly less expensive. Both Richmond and Danville benefitted from increased trade. Farmers in northern North Carolina carried more of their crops to Danville, where the tobacco processing factories grew. Tobacco processing also increased in Richmond, and wheat from the Piedmont helped expand the flour mills that were using hydropower at the Fall Line.
The Richmond and Danville Railroad proposed to build beyond Danville and lay track through North Carolina, but the legislature in that state would not issue a charter to the Virginia company. In 1849, the North Carolina General Asssembly authorized construction of the North Carolina Railroad to carry trade from Charlotte to Goldsboro. That was designed to keep the traffic originating within North Carolina, at farms or furnaces, flowing to a North Carolina port.
North Carolina did authorize the Dan River Coalfield Railroad to build from the state line to the coal-mining area in the Danville Basin. However, that railroad could not build within 20 miles of the North Carolina Railroad.
Efforts by the Richmond and Danville Railroad to build a link from Danville to Greensboro, which would allow traffc from North Carolina to go to a port on the Chesapeake Bay in Virginia, were unsuccessful until the Civil War. In 1862, "national" considerations were viewed as more important than a state's right to charter railroads within the state. The Confederate Congress authorized the Piedmont Railroad to link Danville to the North Carolina Railroad at Greensboro.
The Richmond and Danville Railroad purchased almost all the stock and built the line. As required by North Carolina, the track was built to a 4-foot, 8.5 inch gauge. The Richmond and Danville had a 5-foot gauge, so all passengers and freight had to transfer at Danville until the Piedmont Railroad gauge was changed to 5-foot in 1866. Twenty years later, both railroads switched to the new standard of 4-foot, 8.5 inch.1
Philip Stanley, "Legislating the Danville Connection, 1847-1862: Railroads and Regionalism versus Nationalism in the Confederate States of America," Masters thesis, Virginia Commonwealth University, 2014, pp.46-47, https://scholarscompass.vcu.edu/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=4497&context=etd; "Danville and the Steam Railroad," Bits of History, March 25, 2018, http://hisbits.blogspot.com/2015/02/danville-and-steam-railroad.html; "North Carolina Railroads - Roanoke Valley Railroad," Carolana, http://www.carolana.com/NC/Transportation/railroads/nc_rrs_roanoke_valley.html (last checked July 2, 2020)
The Richmond and Danville Railroad was reconstructed and expanded after the Civil War. In Richmond, a bridge was completed around 1870 to connect Belle Isle to the Tredegar Iron Works on the north bank of the James River. That extended the spur built in 1852 from the southern bank to the island.1
"Belle Isle History," Richmond Riverfront Plan, November 26, 2012, https://www.rva.gov/sites/default/files/2019-10/2_Belle_Isle.pdf (last checked October 13, 2025)
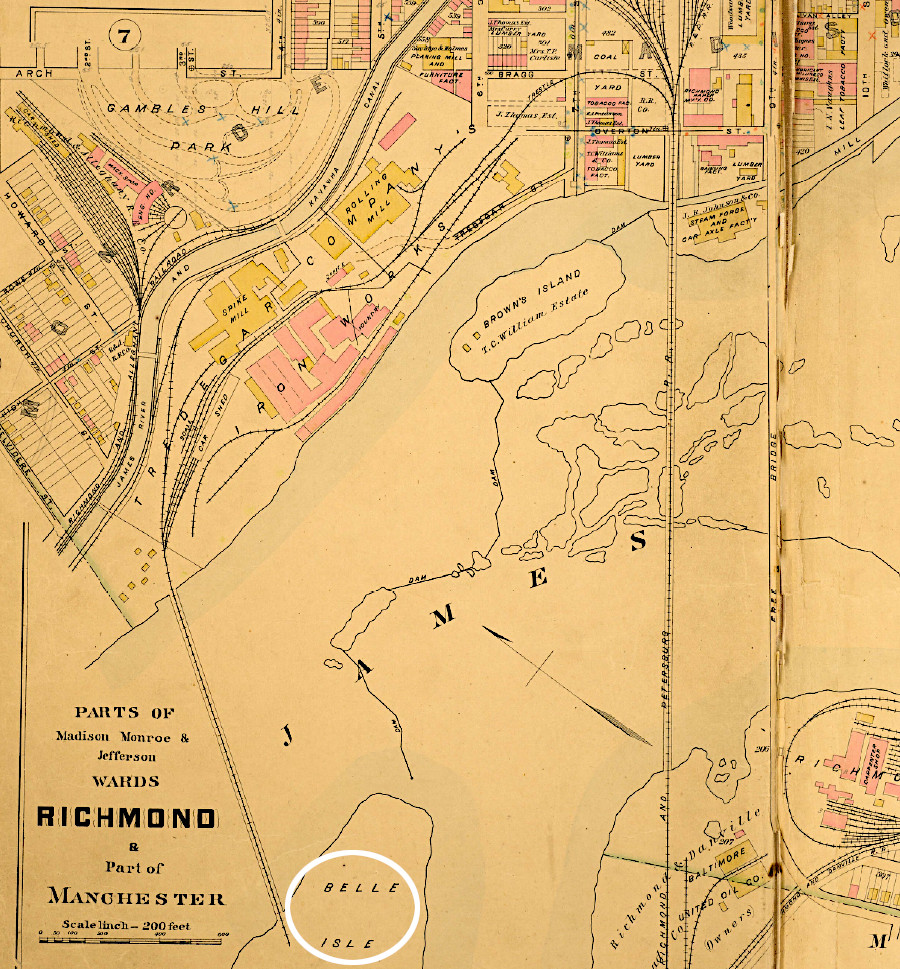
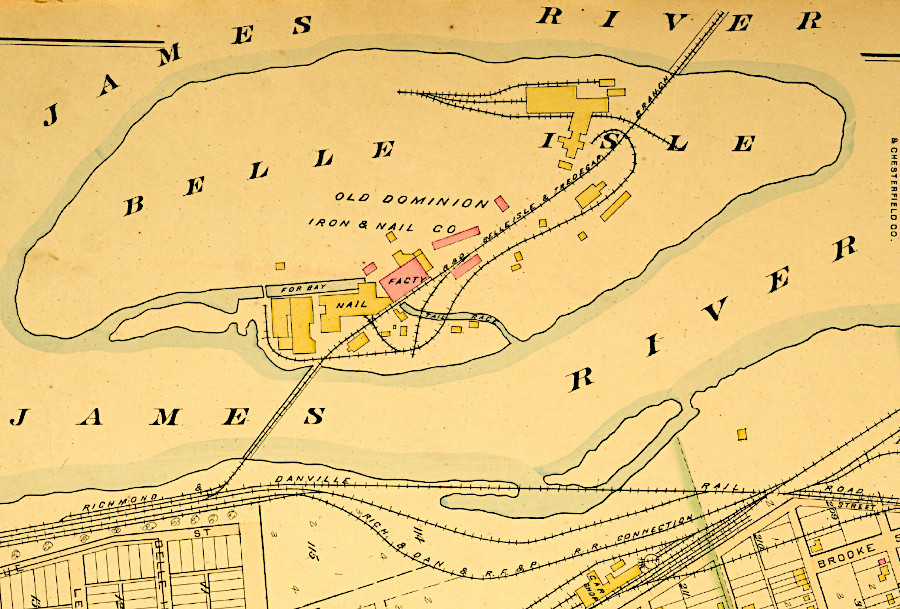
soon after the Civil War, the Richmond and Danville Railroad built a bridge connecting Belle Isle to the north bank of the James River
Source: Virginia Commonwealth University (VCU), Baist Atlas of Richmond, VA (1889)
The Pennsylvania Railroad sought to outmaneuver the Baltimore and Ohio Railroad after the Civil War to establish dominance in the southern states. Starting in 1871, the Pennsylvania Railroad used its 1/6th ownership of the Southern Railway Security Company, a holding company that was technically not a railroad, to gain some control over the Richmond and Danville Railroad, North Carolina Railroad, and Atlanta and Richmond Air Line Railway (which connected Charlotte to Atlanta in 1873).
That holding company allowed coordination of rates and operations, and through its holding company the Pennsylvania Railroad established the Piedmont Air Line. New track was built in 1873 to finally connect the Richmond and Danville Railroad and the Richmond, York River and Chesapeake Railroad in Richmond, allowing customers to ship cotton from Atlanta to the deepwater port on the York River at West Point. That year, the Southern Railway Security Company sold its shares in the Richmond and Danville Railroad to the Pennsylvania Railroad, giving it clear control.1
Fairfax Harrison, A History of the Legal Development of the Railroad System of Southern Railway Company, 1901, pp.88-96, https://books.google.com/books?id=0IkjAQAAMAAJ; H. W. Schotter, The growth and development of the Pennsylvania Railroad Company, Press of Allen, Lane & Scott, 1927, pp.110-111, https://hdl.handle.net/2027/uc1.$b38943 (last checked July 2, 2020)
However, railroad traffic in the former Confederate states was not sufficient to generate the profits desired by the Pennsylvania Railroad. In 1880, it sold its shares in the Richmond and Danville Railroad. In a complicated financial arrangement, the Richmond and West Point Terminal Railway and Warehouse Company ("the Terminal") was formed as another holding company which could own a majority of the stock in multiple railroads. The new Richmond and West Point Terminal Railway and Warehouse Company obtained control of a network of southeastern railroads, peaking at 3,300 miles of track.
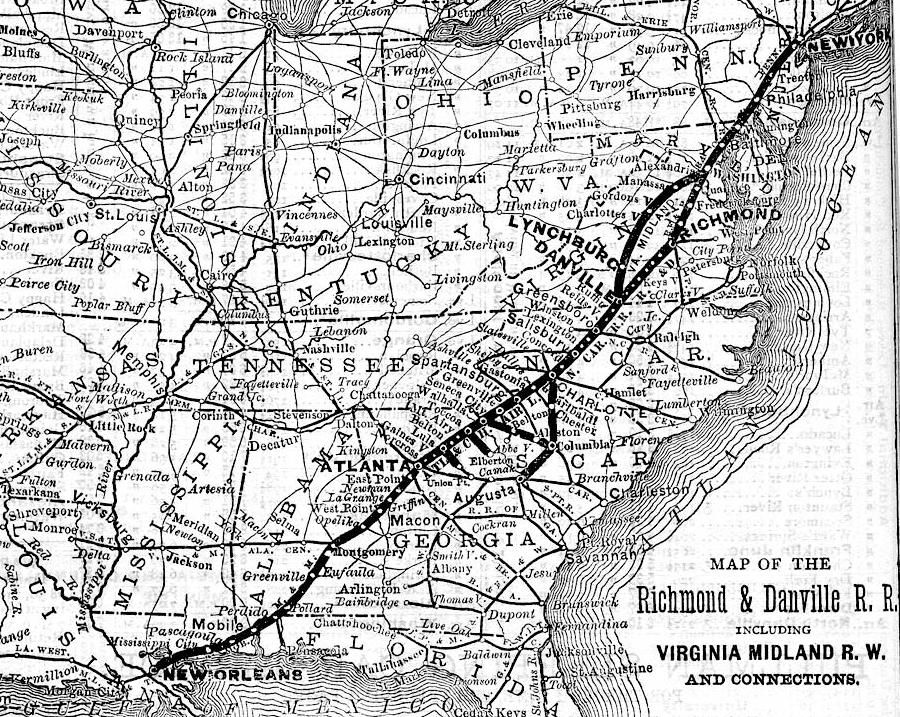
the Richmond and Danville Railroad and the Terminal controlled a network of lines extending into the southern states
Source: Wikipedia, Richmond and Danville Railroad (Travelers' Official Railway Guide for the United States and Canada, September, 1882)
The Terminal replaced the short-lived Southern Railway Security Company, which had established how railroads could be consolidated but had not established close operational coordination between the lines it controlled. Northern investor created new financial vehicles to take advantage of the depressed prices of Southern railroads. Through manipulating the sale of railroad stocks and bonds, and by shifting control of different assets, investors sought to make profits primarily from asset appreciation. Expanding the effciency or the revenues of different railroads, as the economies of Southern states recovered, was a low priority for the Terminal.
As described later by Fairfax Harrison:
The stockholders of the Richmond and Danville Railroad overlapped with the stockholders of the the Terminal. They had the option of having the Terminal gain control of a railroad, or having just the Richmond and Danville Railroad lease it. Financial considerations drove the decisions on purchasing stock, but the financiers did not presume to know how to operate a railroad. The operational managers of the Richmond and Danville Railroad had the authority to synchronize train schedules of trains and manage all technical details.
In 1881, the Richmond and Danville Railroad leased the Richmond, York River and Chesapeake Railroad. That simplified shipping from Greensboro via rail to the deepwater port at West Point. A steamship line was started to provide freight and passenger service from West Point, and other arrangemnts made with the Clyde line that provided steamship connections between Norfolk and New York/Philadelphia.
Northern financiers arranged for the Richmond and Danville Railroad to own a majority of the Richmond and West Point Terminal Railway and Warehouse Company stock in 1884. When the stockholders in "the Terminal" wanted to extract profits, they sold more stock. To maintain control of the holding company, the owners of stock in the Richmond and Danville Railroad had to purchase at least half of the new shares.
In 1886, financiers reversed the roles of the Richmond and Danville Railroad and the Richmond and West Point Terminal Railway and Warehouse Company. The Terminal ended up owning the railroad. Leases of other railroads were transferred from the Terminal to the Richmond and Danville Railroad, including control of the Virginia Midland; Franklin and Pittsylvania; Washington, Ohio and Western, and Clarksville and North Carolina railroads in Virginia. The Terminal retained ownership of the Danville and Western Railway, but the Richmond and Danville Railroad operated it.
One description of the financial deals by the directors of "The Terminal" is blunt about dishonest transactions:2
John Moody, The Railroad Builders: A Chronicle of the Welding of the States, Yale University Press, 1919, p.49, https://archive.org/details/railroadbuilder00mood (last checked July 27, 2020)
The 1892 "panic" or economic recession disrupted the house of cards which had been assembled to finance the Terminal and the Richmond and Danville Railroad. Revenues dropped, mortgages could not be paid, and lease commitments were ended. In the following major reorganization of the rail network in southern states, the Richmond and Danville Railroad became part of the Southern Railway in 1894.2
"North Carolina Railroads - Richmond & Danville Railroad," Carolana, http://www.carolana.com/NC/Transportation/railroads/nc_rrs_richmond_danville.html; Fairfax Harrison, A History of the Legal Development of the Railroad System of Southern Railway Company, 1901, p.97, pp.100-103, p.115, pp.566-567, https://books.google.com/books?id=0IkjAQAAMAAJ (last checked June 22, 2020)
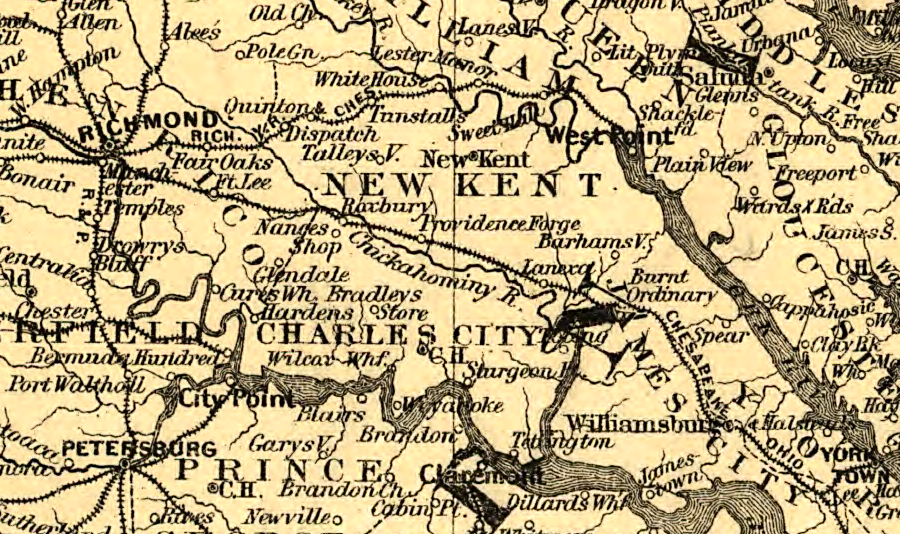
the Richmond and Danville had access to wharves on the York River at West Point, while the Chesapeake and Ohio built a line to Newport News
Source: Library of Congress, Map showing the Albemarle & Pantego Railroad and its connections (G.W. & C.B. Colton & Co, 1887)
The Southern Railway merged with the Norfolk and Western Railroad in 1982. Portions of the old Richmond and Danville route were no longer needed. Segments southwest of Burkeville were abandoned, or converted into the Virginia Southern short line railroad.
The stretch between Ringgold and Keysville was abandoned in 1988. The 5.5-mile long Richmond and Danville Rail-Trail, also known as the Ringgold Trail, opened in 2001. In 1018, it was heavily damaged by Hurricane Michael, washing off gravel and eroding gaps that made the trail unsuitable for cyclists.2
"Tobacco Heritage Trail History," TrailLink, https://www.traillink.com/trail-history/tobacco-heritage-trail/; "Richmond and Danville Rail-Trail," TrailLink, https://www.traillink.com/trail/richmond-and-danville-rail-trail/ (last checked December 15, 2020)
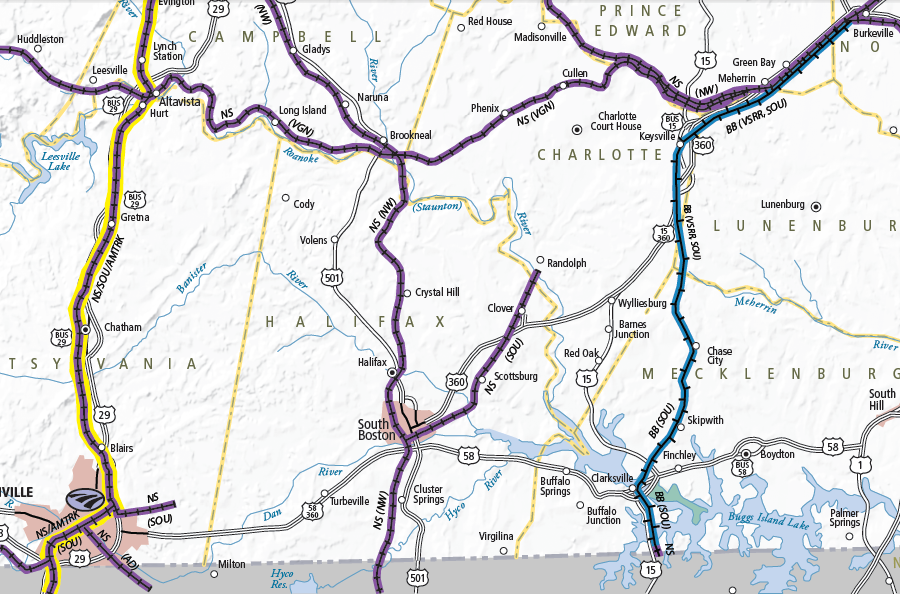
the Richmond and Danville had access to wharves on the York River at West Point, while the Chesapeake and Ohio built a line to Newport News
Source: Virginia Department of Rail and Public Transportation (DRPT), Virginia Rail Map (2012)
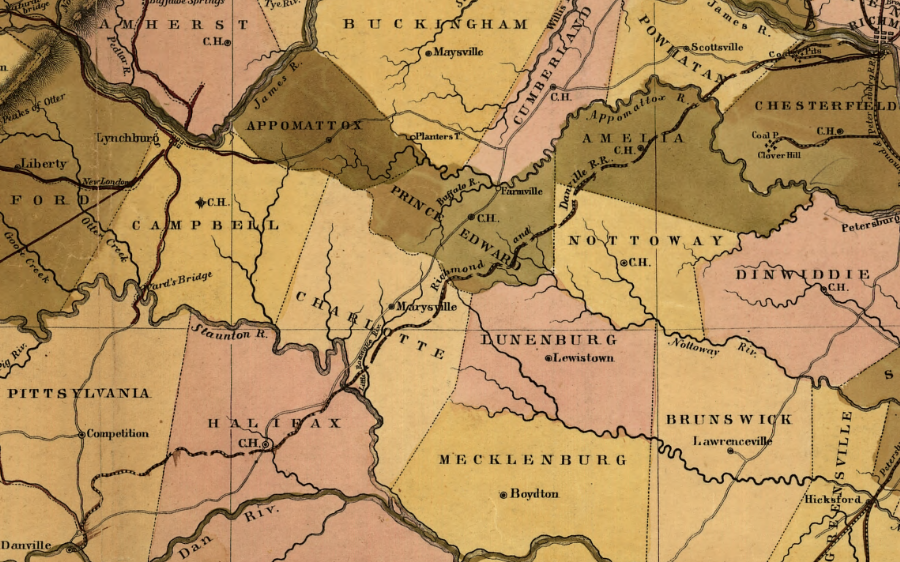
in 1848, the Richmond and Danville Railroad was under construction
Source: Library of Congress, A map of the internal improvements of Virginia (Claudius Crozet, 1848)
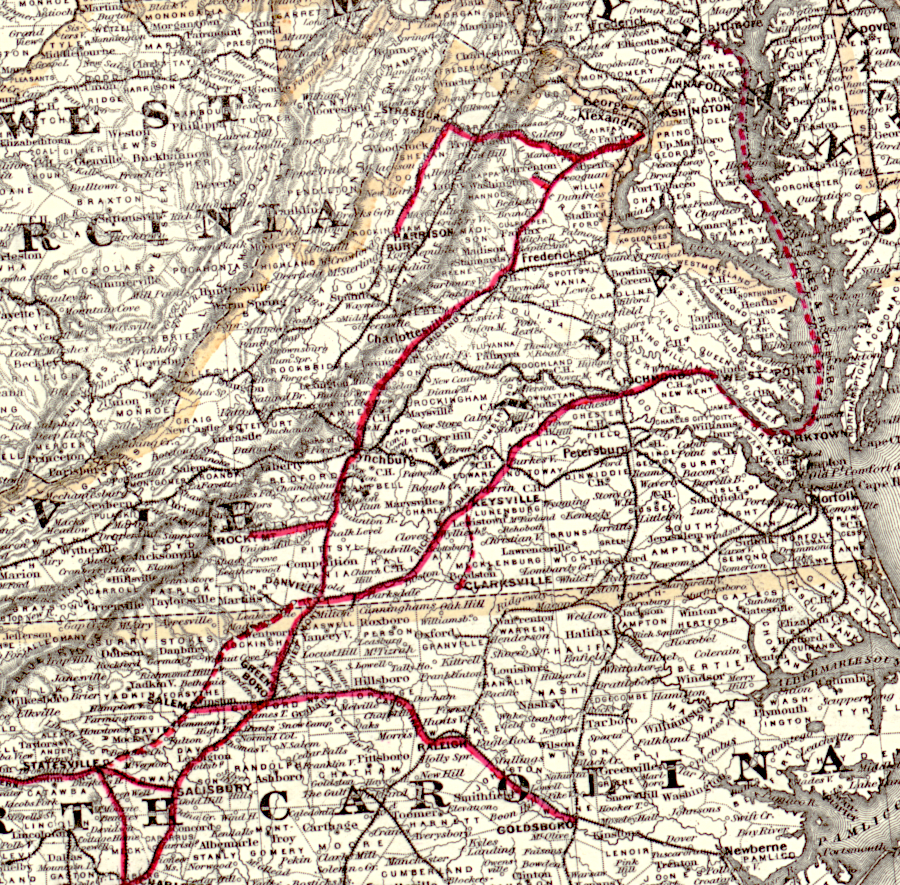
the Richmond and Danville system in 1881 extended south towards Atlanta
Source: Library of Congress, Map of the Richmond & Danville Railroad system (G.W. & C.B. Colton & Co, 1881)
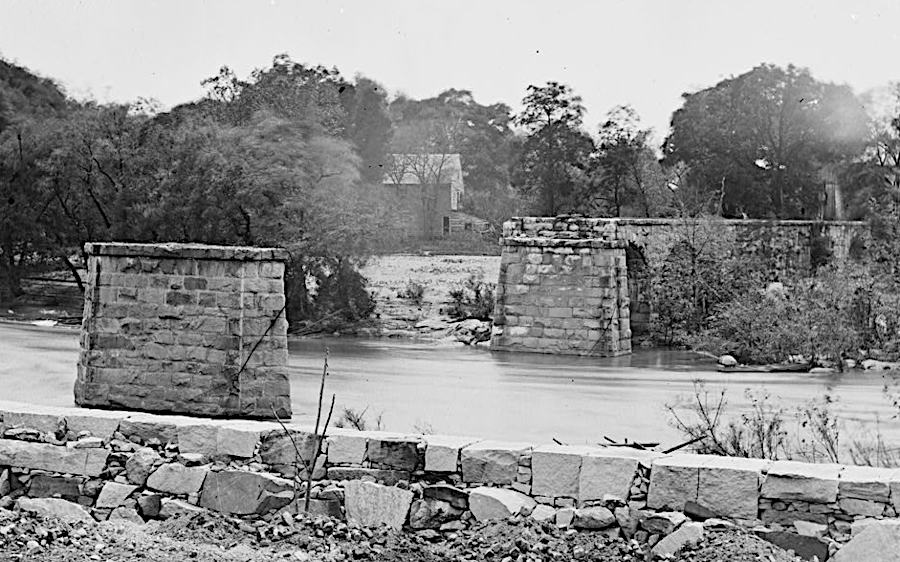

the Richmond and Danville Railroad bridge over the James River was destroyed in the evacuation fire on the night of April 2, 1865
Source: Library of Congress, Richmond, Virginia. Ruins of Richmond & Danville Railroad bridge (1865)
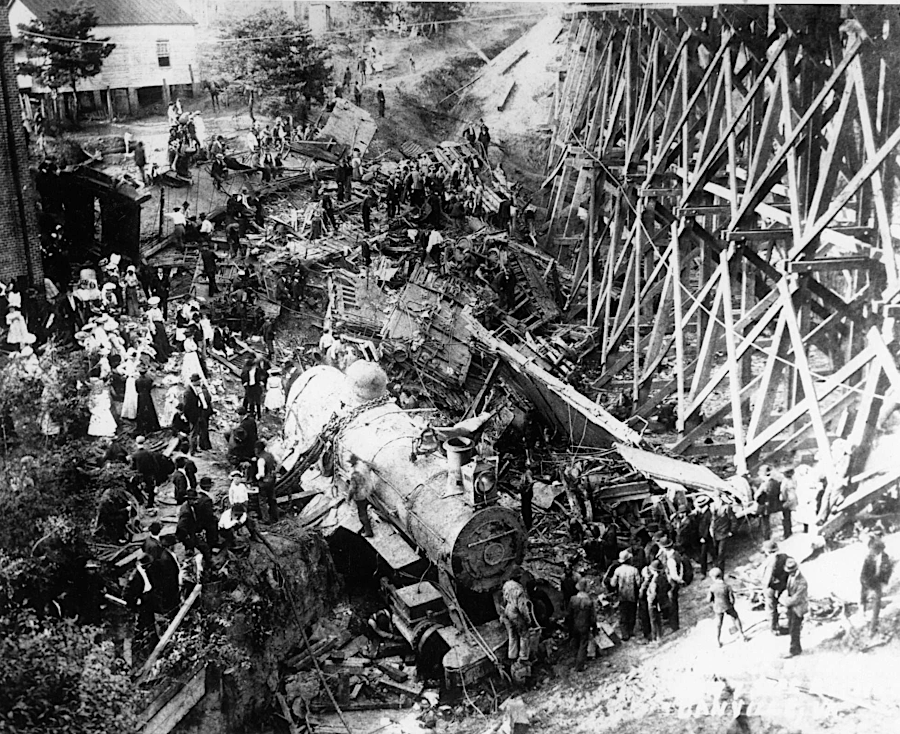

11 people died when Old 97 ran off the rails at Stillhouse Trestle near Danville on September 27, 1903
Source: Encyclopedia Virginia, Wreck of the Old 97 (1903)

the Richmond and Danville Railroad hired enslaved people from their white owners
Source: Library of Congress, Chronicling America, The Daily Dispatch (August 2, 1862)