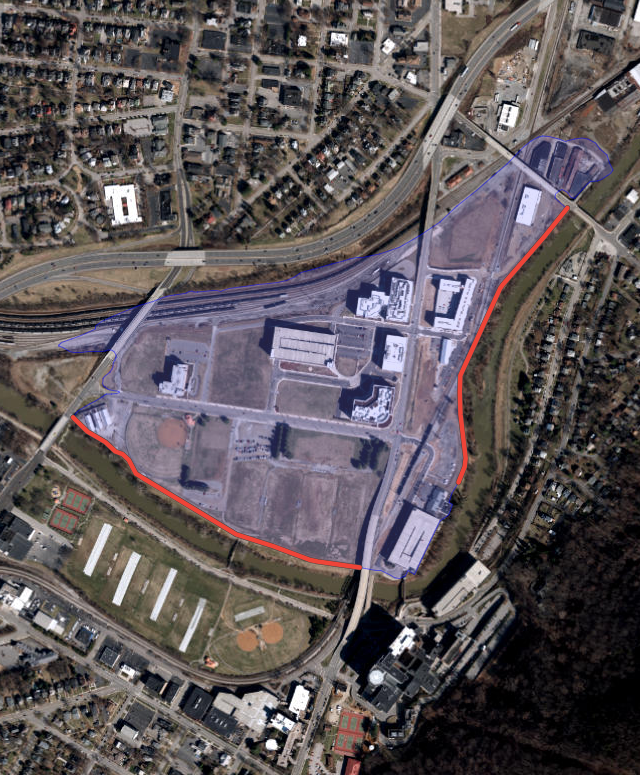
Training Wall 330, part of the Roanoke River Flood Reduction Project (FRP), was completed in 2009
Source: US Army Corps of Engineers National Levee Database, Roanoke FRP

Training Wall 330, part of the Roanoke River Flood Reduction Project (FRP), was completed in 2009
Source: US Army Corps of Engineers National Levee Database, Roanoke FRP
In Virginia, the US Army Corps of Engineers has documented 21 levee systems with 16 miles of levees and 376 levee structures.1
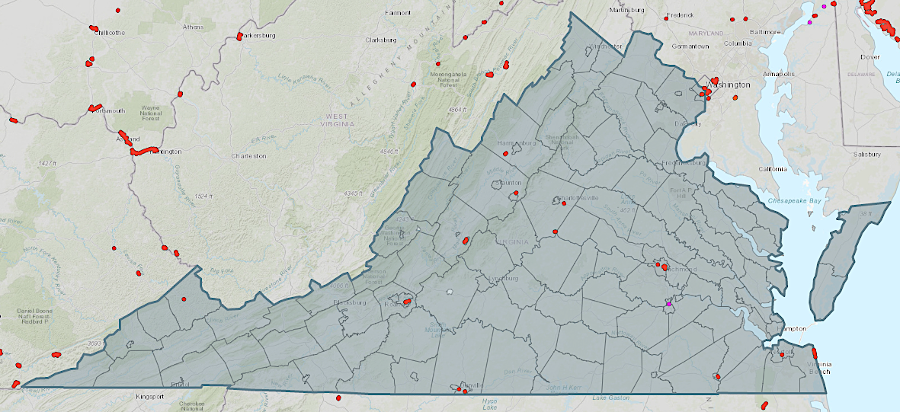
levees in Virginia are primarily along inland rivers, not at the oceanfront
Source: US Army Corps of Engineers National Levee Database, Levees of Virginia
World war I triggered rapid development in Arlington County and the City of Alexandria. Arlington County's population grew 60% between 1910-1920, and another 40% in the next decade. The creation of impervious surface produced a new runoff pattern, with stormwater flowing off properties rather than soaking into the ground during rainstorms. The channel of Four Mile Run was no longer adequate to carry away the runoff from within its 20-square mile watershed, and flooding after major storms became routine.
Between 1974-1984, the US Army Corps of Engineers built the Arlington East, Arlington West, Alexandria East, and Alexandria West Flood Risk Management System. The Arlington East component of the project included 950 feet of floodwall and 750 of retaining wall along the left bank of Four Mile Run, plus approximately 560 feet of floodwall and 250 feet of embankment along the left bank of Long Branch. The Alexandria East component included 580 linear feet of embankment, 1500 linear feet of floodwall, 480 linear feet of retaining wall, and 10 drainage structures. The embankment was only 0.5 to 2.5 feet high, but that met design requirements.
The project was designed to contain the flow of a 100-year flood. Erosion steadily carried sediment into the channel, so in 2022-23 Arlington County and the City of Alexandria had to pay for a $5 million project to dredge out the accumulated material. Otherwise, the floodwall and embankment would be overtopped by water in a future 100-year flood.2
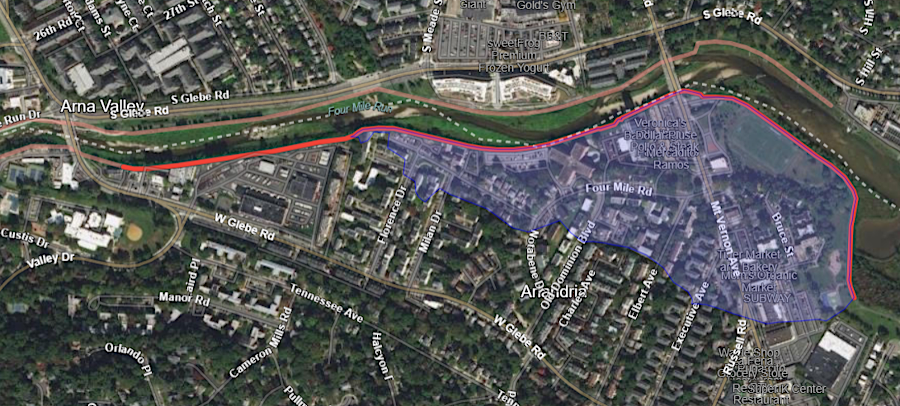
the 1974-84 Alexandria East project along Four Mile Run included a leveee 0.2 to 2.5 feet high, as well as a floodwall
Source: US Army Corps of Engineers National Levee Database, Alexandria East
The Corps of Engineers completed a Metropolitan Washington, District of Columbia Coastal Storm Risk Management Study in 2022 that recommended more flood control structures. According to the Federal agency, the Arlington County wastewater treatment plant needed a floodwall along Four Mile Run while the Belle Haven neighborhood in Fairfax County needed both a floodwall and a levee.3
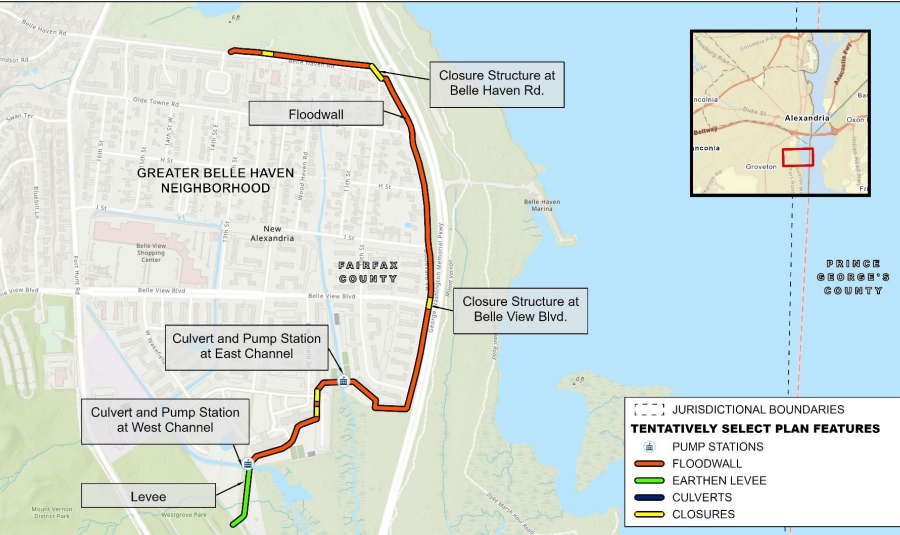
in 2022, a levee was proposed as part of the flood control project that could protect Belle Haven in Fairfax County
Source: US Army Corps of Engineers, Metropolitan Washington, District of Columbia Coastal Storm Risk Management Study (Figure E-2)