Virginia's Western "Frontier" Forts After 1750
Since English colonists arrived in Virginia, they built forts to protect themselves from attack. The need for such protection was demonstrated at Jamestown within the first month of settlement.
After fortifying Jamestown, colonists built forts at Point Comfort, the mouth of the Hampton River, and at the planned new capital of Henricus. After the start of the Second Anglo-Powhatan War in 1622, the Peninsula was fortified. As settlement spread westward, additional forts were built at the Fall Line.1
Even before the Piedmont was settled, Scotch-Irish and German-speaking immigrants migrated south from Pennsylvania into the Shenandoah Valley starting in the 1730's. Their settlements disrupted the hunting expeditions of the Delaware, Shawnee, and Mingo. Raiding parties of the Haudenosaunee and Cherokee had to avoid the new settlements, or sometimes killed livestock for food while traveling.
Land speculators in Virginia with political connections in the General Assembly and with the governor saw great opportunity in getting royal grants to vast amounts of land west of the Allegheny Front. Using title granted by the British government to hundreds of thousands of acres, the speculators would get richer by surveying and selling parcels in roughly 100-acre chunks to new settlers.
For the large land companies to attract settlers, Native American claims to the land had to be extinguished through private sales or through official government treaties.
After the Haudenosaunee agreed to the Treaty of Lancaster in 1744, Virginia's governors approved more land grants west of the Blue Ridge. The Wood's River Grant was issued in 1745, and the Ohio Company and the Loyal Land Company received grants in 1749.2
At the start of the French and Indian War, there were already settlers in the New River near modern-day Radford and a few in the headwaters of the Tennessee River. Individual houses provided protection against attack by the Shawnee or Cherokee.
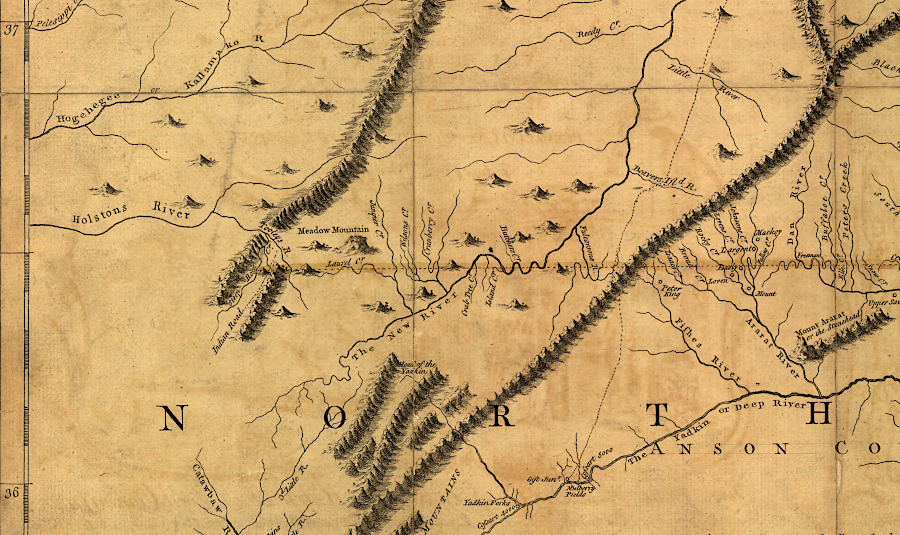
before settlers reached the Tennessee River watershed during the French and Indian War, colonists had no need to build forts there
Source: Library of Congress, A map of the most inhabited part of Virginia containing the whole province of Maryland with part of Pensilvania, New Jersey and North Carolina. (by Joshua Fry and Peter Jefferson, 1755)
Some pioneers were unwilling to wait for a legal process that would minimize resistance by the indigenous people who lived nearby and hunted throughout the Ohio River watershed. Squatters ignored the issue of ownership, anticipating that their occupation of good bottomlands could be legalized later.
By the middle of the French and Indian War, there were hundreds of small farms in the Holston River and Clinch River watersheds. Many assumed they were located in Virginia, but the boundary line with the North Carolina colony was undefined. The primary issue for those settlers was getting the Cherokee to accept the settlements rather than to attack them.
Fort Loudoun was constructed in 1756-67 by South Carolina militia, who wanted to maintain the fur trade of the Overhill Towns of the Cherokee with Charles Town. The peace between colonists and the Cherokee ended in 1760. South Carolinians massacred Cherokee chiefs being kept as hostages at Fort Prince George. (The site of Fort Loudoun is now underneath Tellico Lake, while Fort Prince George is beneath Lake Keowee.)
The Cherokee then besieged and captured Fort Loudoun.
After Braddock's defeat in 1755 near Fort Duquesne, all British forces who had arrived with Braddock retreated into Pennsylvania. Once again, the Virginia colony had to rely upon its own resources to deal with a Native American war.
The General Assembly in Williamsburg recycled the defensive strategy adopted in 1676 - build a series of forts to protect farms and settlements. That strategy had been an absolute failure, back when the frontier was further east at the boundary of the Piedmont and Coastal Plain. The failure of colonial leadership to protect the colonists led to Bacon's Rebellion, when the colonial capital of Jamestown was burned and Gov. William Berkeley was forced to flee to the Eastern Shore.
Gov. Dinwiddie appointed George Washington as head of the Virginia militia. Washington recognized that forts located 20 miles from each other offered little protection to most settlers, who would be captured/killed before they could flee to safety. A line of widely-scattered forts would not be an effective barrier to Shawnee raids, so Washington wrote Governor Dinwiddie in early 1756:2
- It seemed to be the sentiment of the House of Burgesses when I was down, that a chain of forts should be erected upon our frontiers, for the defence of the people. This expedient, in my opinion, without an inconceivable number of men, will never answer their expectations.
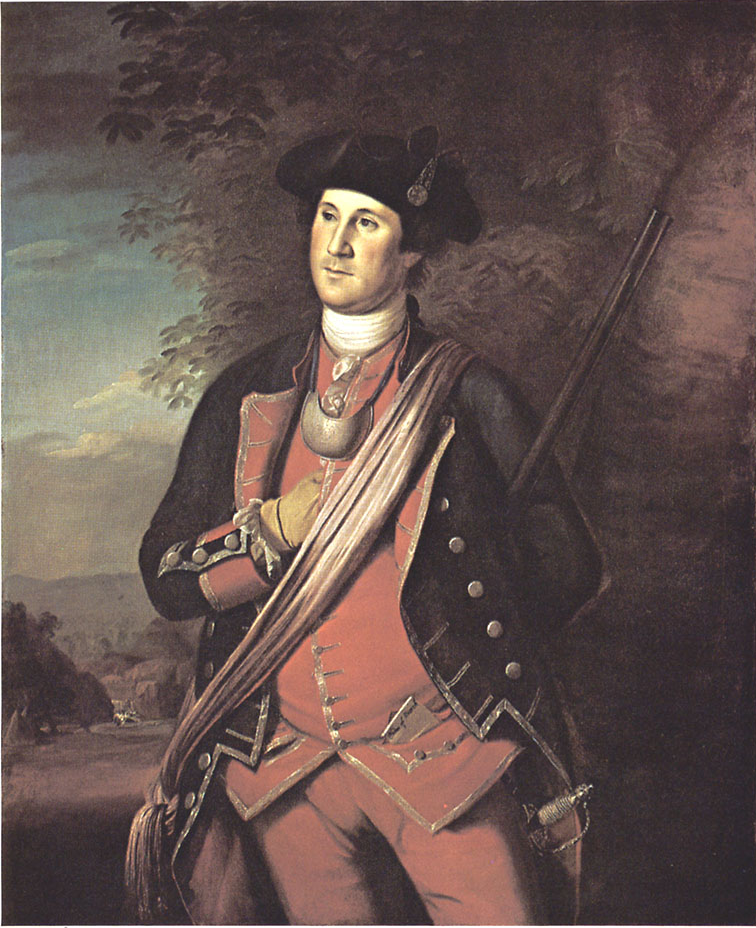

George Washington, dressed in his Virginia militia uniform
Source: Library of Congress, George Washington Papers
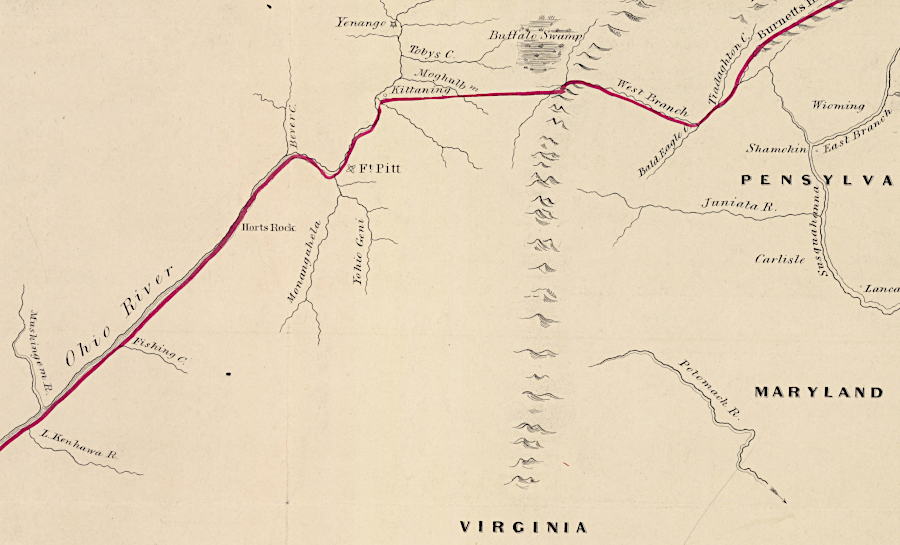
after the 1768 Treaty of Fort Stanwix, Fort Pitt was on the edge of authorized colonial settlement
Source: Library of Congress, Cantonment of His Majesty's forces in N. America according to the disposition now made & to be compleated as soon as practicable taken from the general distribution dated at New York 29th. March 1766
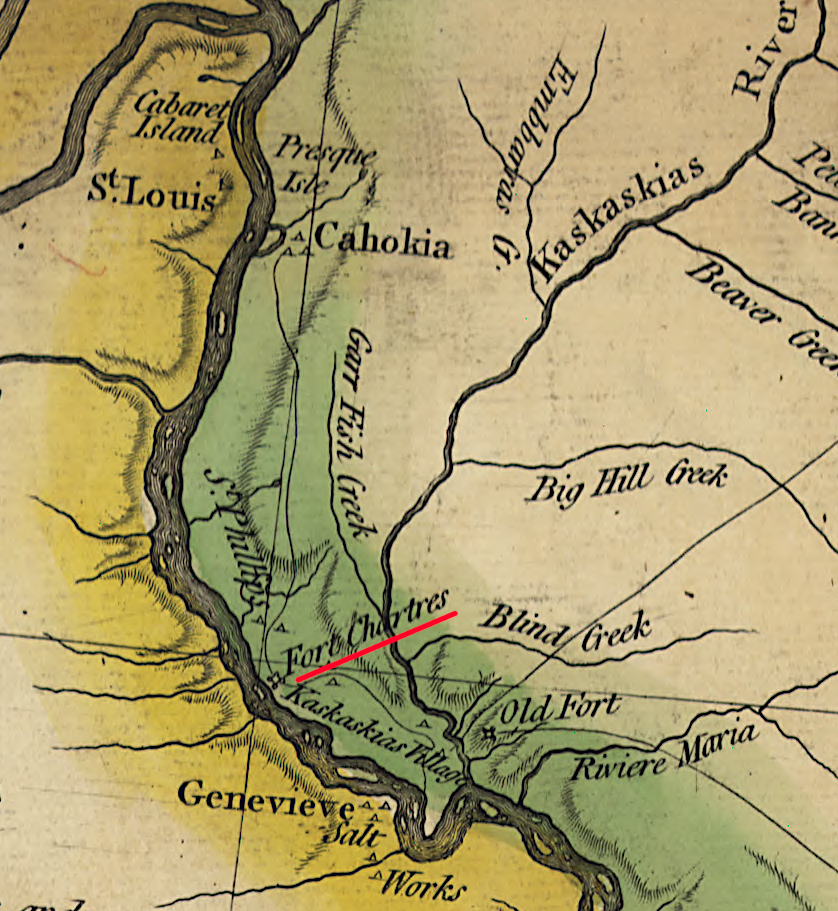
General Gage closed Fort Chartres in 1772 in order to reduce the costs of maintaining the British army in North America
Source: William L. Clements Library, University of Michigan, Map of the frontiers of the northern colonies with the boundary line established between them and the Indians at the treaty held by S. Will. Johnson at Ft. Stanwix in Novr. 1768 (by Guy Johnson)
Links
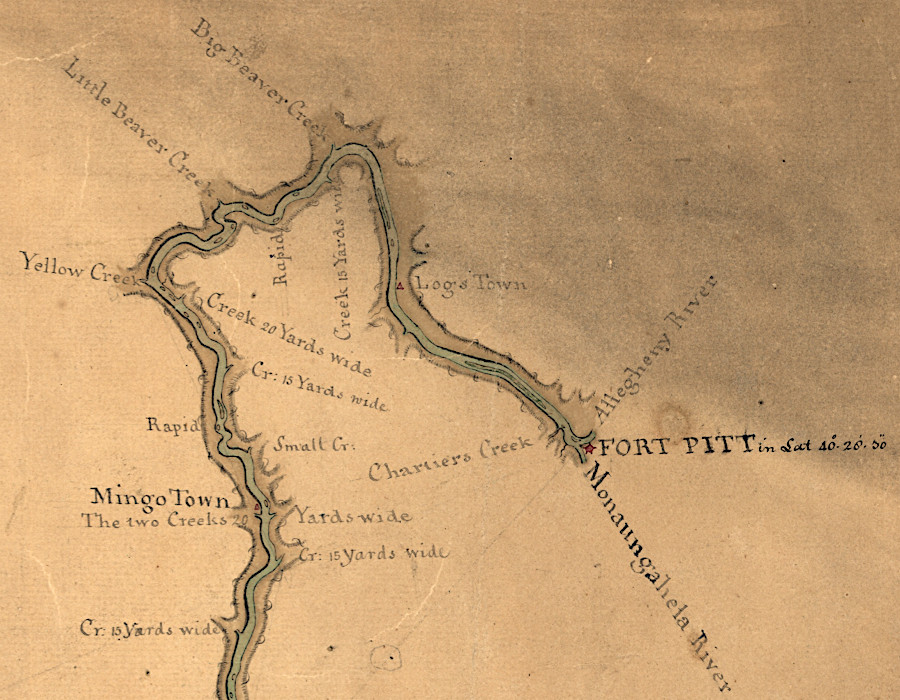
western forts were close to Native American towns, and centers of trade and interaction between colonial and Native American societies
Source: Library of Congress, Map of the Ohio River from Fort Pitt (by John Montrésor, 1776)
References
1. "Fort Site," Jamestown Discovery, https://historicjamestowne.org/visit/plan-your-visit/fort-site/?srsltid=AfmBOoo8ITQfSVeRG3ScpESxhJxo-a94Uk0VPuc_e77eGcIdzg8hb9yO (last checked June 8, 2025)
2. "George Washington to Governor Robert Dinwiddie, April 7, 1756," West Virginia Division of Culture and History, http://www.wvculture.org/history/frenchandindian/17560407washington.html (last checked August 1, 2025)
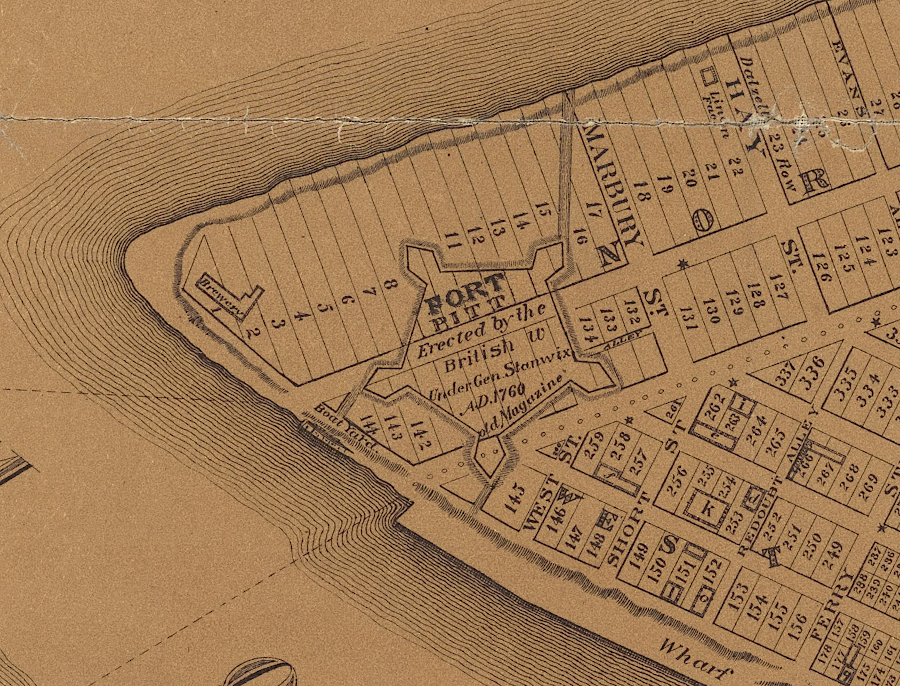
Fort Pitt disappeared quickly after the American Revolution, as the city of Pittsburgh developed
Source: New York Public Library, Map of Pittsburgh and its environs (by Lewis Kenyon, 1830)
The Military in Virginia
Exploring Land, Settling Frontiers
Virginia Places





